Is the Fed worried about bank reserve liquidity?
Something very interesting showed up in the FOMC November meeting minutes this week
This is a segment from the Forward Guidance newsletter. To read full editions, subscribe .
Something very interesting showed up in the FOMC November meeting minutes this week that had nothing to do with rate cut expectations.
Hidden deep in the minutes was the following excerpt:

Newsletter
Subscribe to Forward Guidance Newsletter
Essentially, the Fed is considering lowering the award rate on Reverse Repo Facility assets by 5-basis points, which would lower the bottom of the target range of the federal funds rate band.
Here is what that complex looks like visually:
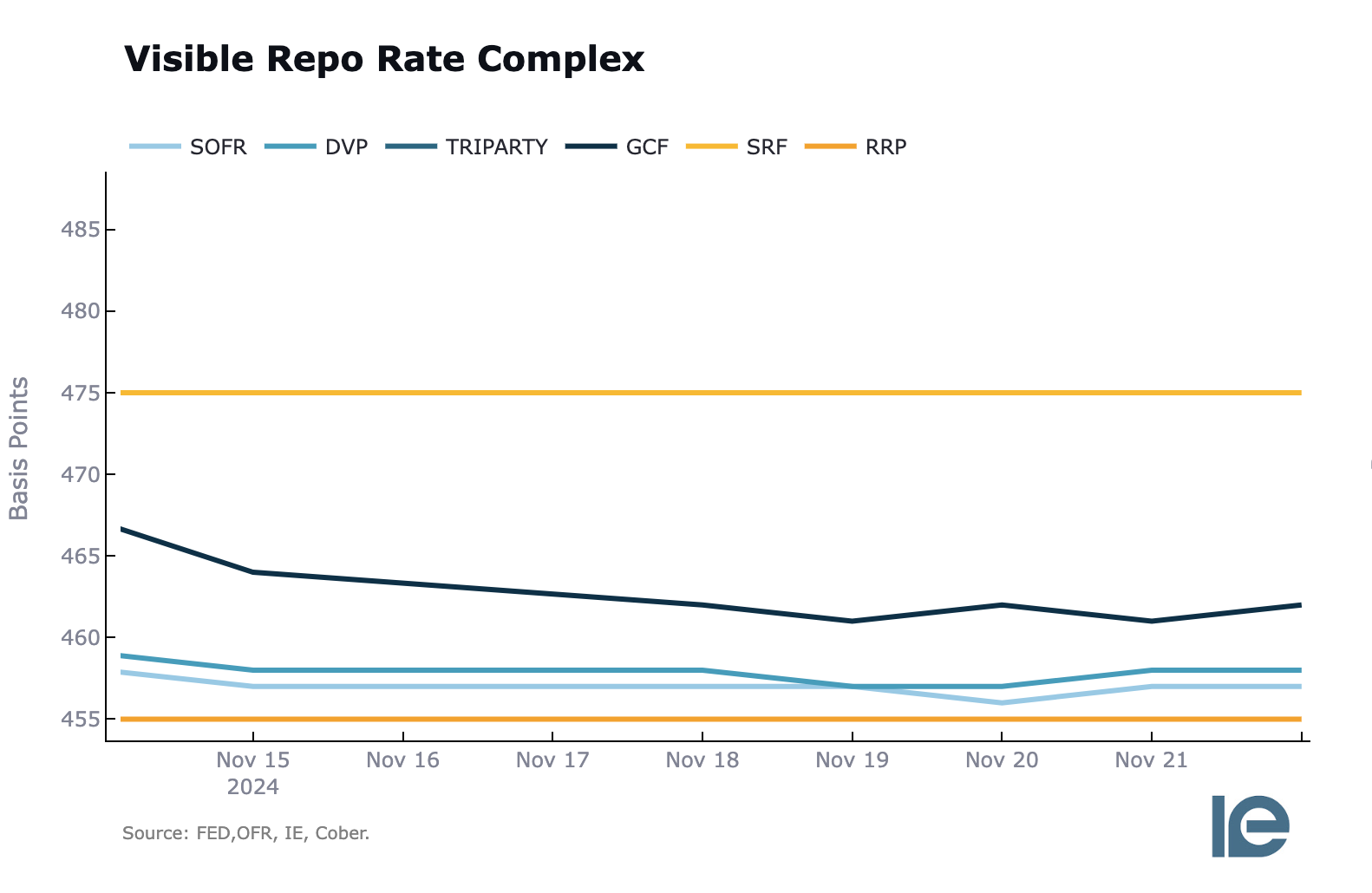
One can only speculate as to why the FOMC wants to lower this rate, but there’s a convincing theory:
Given the recent uptake in the Standing Repo Facility that occurred at the end of the previous quarter, paired with FOMC members acknowledging that the clock is ticking on how much longer QT can continue without potential strain showing up in the monetary plumbing system, the FOMC might be trying to get ahead of this by encouraging outflows from the RRP and increasing bank reserves to provide ample liquidity.
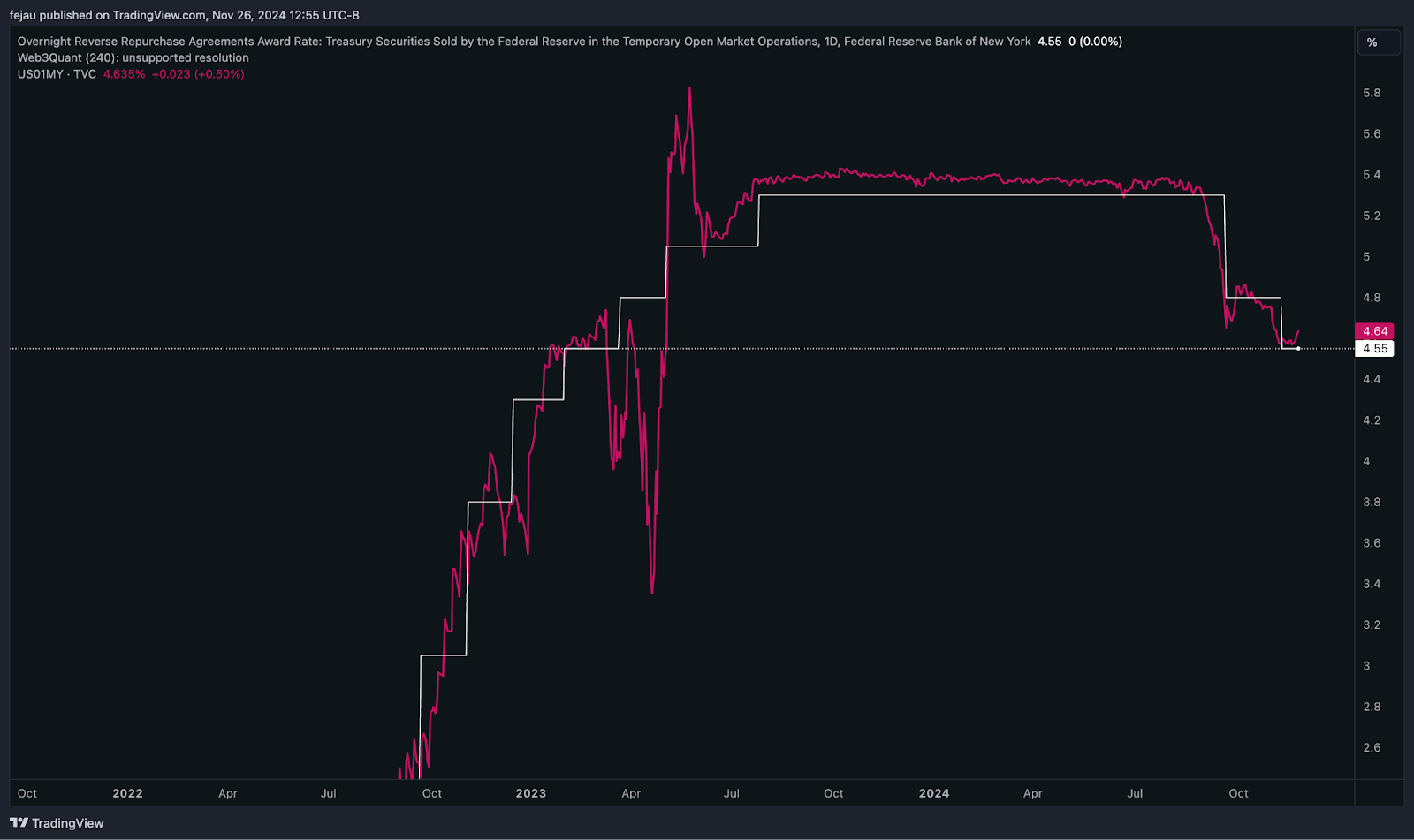
As shown in this chart comparing the $1 million T-bill with the RRP award rate, money market funds are generally alternating between owning the two, depending on which has the higher yield at the time. By decreasing the award rate, T-bills are made more attractive:
As we can see in the current balance of the RRP, there’s still $186 billion of cash that is “stuck” in the RRP. By lowering the award rate, it appears the FOMC is trying to get this money into the broad financial system to ensure liquidity remains ample. This comes in the face of ongoing QT that is getting closer to a potential target that could strain bank reserve levels:
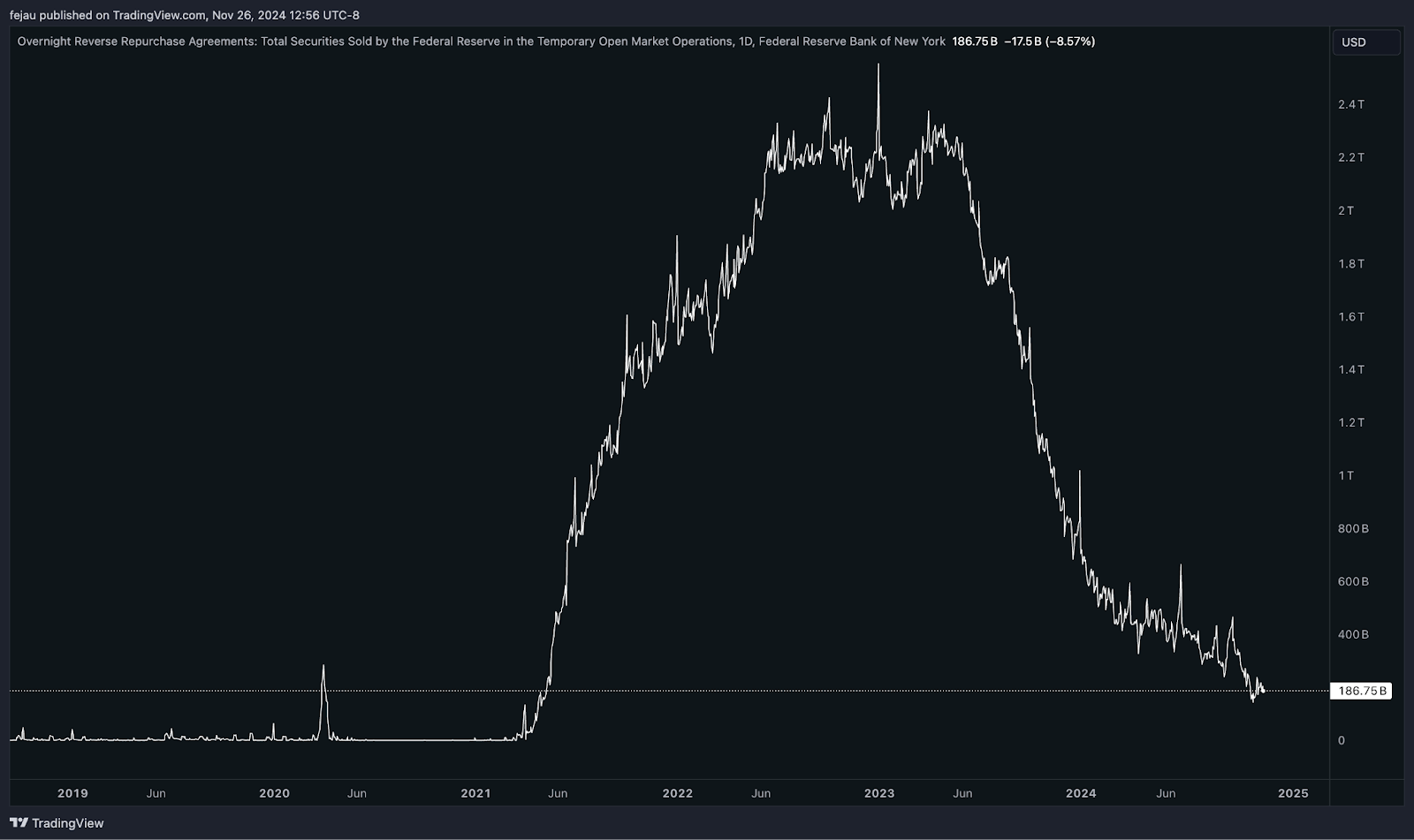
We will need to wait until the next FOMC meeting in December to confirm if this will indeed be the case. The fact is, though, that by even acknowledging this potential dynamic, the FOMC is signaling that they are becoming increasingly concerned about bank reserve liquidity levels.
Start your day with top crypto insights from David Canellis and Katherine Ross. Subscribe to the Empire newsletter .
Explore the growing intersection between crypto, macroeconomics, policy and finance with Ben Strack, Casey Wagner and Felix Jauvin. Subscribe to the Forward Guidance newsletter .
Get alpha directly in your inbox with the 0xResearch newsletter — market highlights, charts, degen trade ideas, governance updates, and more.
The Lightspeed newsletter is all things Solana, in your inbox, every day. Subscribe to daily Solana news from Jack Kubinec and Jeff Albus.
- Banking
- FOMC
- Forward Guidance newsletter
- liquidity
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
You may also like
Last Cycle’s Signal King Murad: 116 Reasons Why the 2026 Bull Market Will Come
I do not agree with the view that the market cycle is only four years; I believe this cycle may extend to four and a half or even five years, and could last until 2026.

Ethereum completes Fusaka upgrade, team claims it can unlock up to 8x data throughput
Major upgrades, which used to take place once a year, are now happening every six months, demonstrating that the foundation still maintains strong execution capabilities despite recent personnel changes.

Glassnode: Is Bitcoin Showing Signs of a 2022 Crash Again? Beware of a Key Range
The current bitcoin market structure is highly similar to Q1 2022, with over 25% of on-chain supply in a loss, ETF capital flows and spot momentum weakening, and the price relying on key cost basis areas.

Crypto Giants Clash: Faith, Utility, and Macro

